
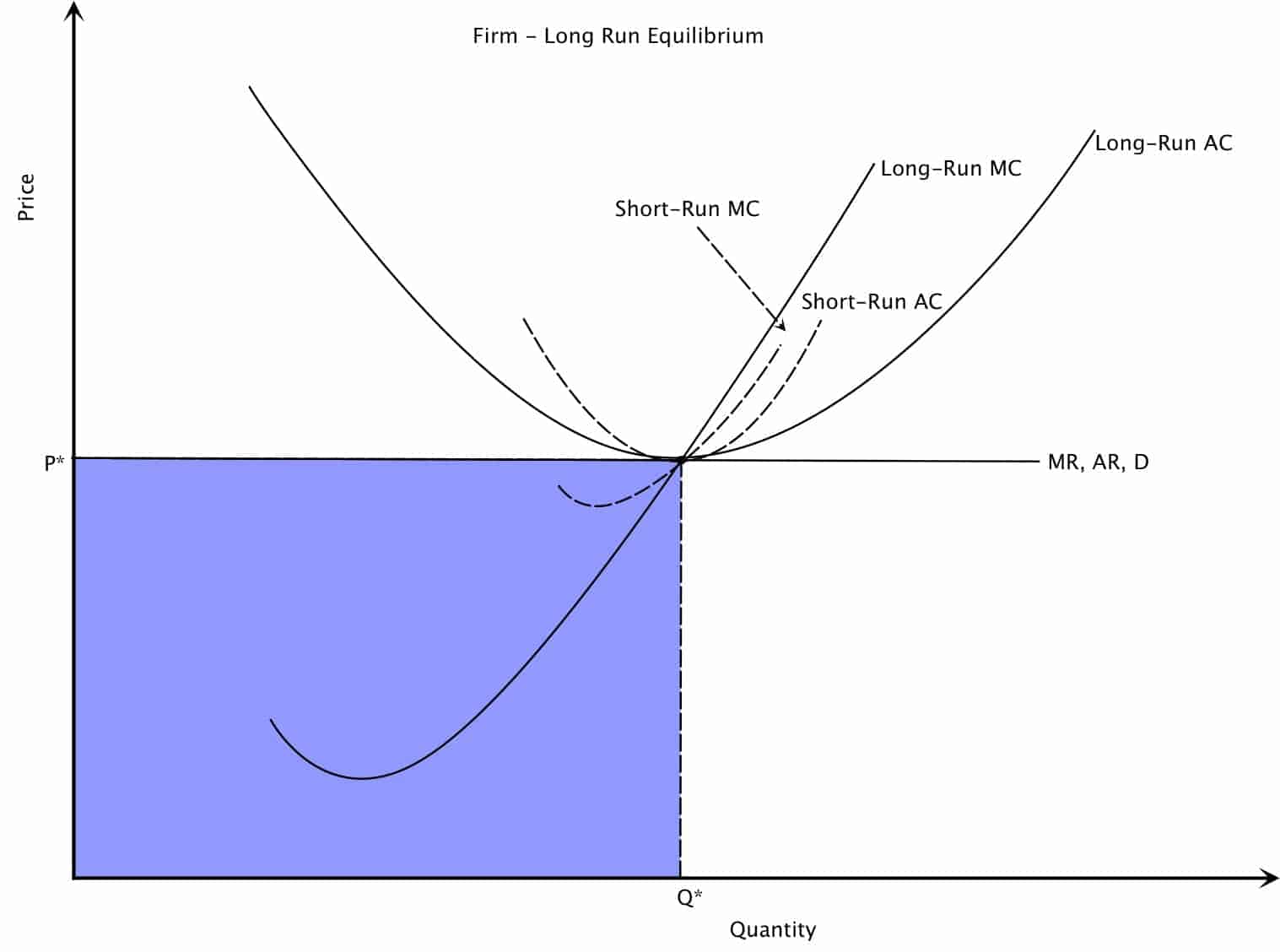
Market Demand: Usually downward sloping, with consumers demanding less when the price is high and more when the price is low.The demand and supply curves for the market and a firm can look similar, but they have important differences: Remember, it’s crucial to distinguish between market demand and supply, and a firm’s demand and supply. Market demand and supply determine the price at which firms sell. These firms are price takers and have no influence over market price. In case you need a refresher, perfect competition refers to a market with numerous firms producing identical products, low barriers to entry, and firms competing solely on the basis of price. So, let’s dive in and learn all about it. Welcome back to our exploration of perfectly competitive markets! In this lesson, we’ll delve into how to determine the optimal price and output for firms operating under perfect competition. A perfectly competitive firm chooses its level of output so that its marginal cost of production equals the market price.Perfect Competition: Optimal Price and Output | CFA Level I Economics If you have no market power, you cannot set a price in excess of marginal cost. The ability to set a price above marginal cost comes from market power. When demand is infinitely elastic, the markup is zero: To see this, go back to the markup formula. But because the price is the same everywhere on the demand curve, picking the best point means picking the best quantity. The seller still picks the best point on the demand curve. Graphically, this means that it is a horizontal line at the market price.Įverything we have shown in this chapter applies to a firm facing such a demand curve. The demand curve faced by a firm in a perfectly competitive market is infinitely elastic. \): The Demand Curve Facing a Firm in a Perfectly Competitive Market


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
